Misc
Misc
Windows
Shortcut Description Ctrl + Tab Change application Ctrl + ~ Change window within an application Browser
Action Shortcut To Address Bar Ctrl + L Scroll between focus panes (e.g. address to bar to body) f6 Open a new window Ctrl + n Open a new window in Incognito mode Ctrl + Shift + n Open a new tab, and jump to it Ctrl + t Reopen previously closed tabs in the order they were closed Ctrl + Shift + t Jump to the next open tab Ctrl + Tab or Ctrl + PgDn Jump to the previous open tab Ctrl + Shift + Tab or Ctrl + PgUp Jump to a specific tab Ctrl + 1 through Ctrl + 8 Jump to the rightmost tab Ctrl + 9 Open your home page in the current tab Alt + Home Open the previous page from your browsing history in the current tab Alt + Left arrow Open the next page from your browsing history in the current tab Alt + Right arrow Close the current tab Ctrl + w or Ctrl + F4 Close the current window Ctrl + Shift + w or Alt + F4 Minimize the current window Alt + Space then n Maximize the current window Alt + Space then x Quit Google Chrome Alt + f then x Move tabs right or left Ctrl + Shift + PgUp or Ctrl + Shift + PgDn
R
Search for R packages
- CRAN table of available packages with descriptions
- List of CRAN Task Views
- Journal of Statistical Software Search
- R-Universe Search
- {packagefinder} - For searching for packages on CRAN
Changelog for RStudio versions
Handling Errors & Warnings in R | List of Typical Messages & How to Solve
Primary CRAN mirror: “https://cloud.r-project.org/”
Detach a package
detach("package:vegan", unload = TRUE)Import functions from package
# R 4.5.0 use("dplyr", c("filter", "select"))- I think this functionality is also available in R4.0+ with
library(pkg, include.only = c("fun1", "fun2")
- I think this functionality is also available in R4.0+ with
If setting up a R environment on a company internet is really slow:
- Sometimes the company uses proxys. You could try to find it out via Proxy settings or the default Browser. In r you can set the parameters via
Sys.setenv(http_proxy ='xxx.xxx.com:80')Same for https_proxy AndNO_PROXY = localhost, 127.0.0.1"(source)- If this works in a live session, put it in your .Rprofile
- Ask IT if they can whitelist cloud.r-project.org and cran.rstudio.com specifically. Many firewalls do deep packet inspection on HTTPS that adds massive latency (source)
- Run RStudio Server on a cloud VM that’s outside the firewall and just access it via browser.
- Sometimes the company uses proxys. You could try to find it out via Proxy settings or the default Browser. In r you can set the parameters via
R-devel (>= 4.4.0) gained a command-line option to adjust the connections limit (previous limit was 128 parallel workers)
$ R > parallelly::availableConnections() [1] 128 $ R --max-connections=512 > parallelly::availableConnections() [1] 512Get installed package names, versions, environment, source (article)
> package_names <- installed.packages()[, 1] > package_data <- lapply( + package_names, + utils::packageDescription, + fields = c("Package", "Version", "Built", "Repository") + ) |> + lapply(as, Class = "list") |> + lapply(setNames, c("Package", "Version", "Environment", "Source")) |> + dplyr::bind_rows()- Environment has OS info, R version, and date installed.
Java Dependent Packages
- {rJavaEnv} - Aims to assist users of all {rJava}-dependent packages by providing functions to quickly install the required Java version and set environment variables.
It downloads non-installer archives of Java, extracts them to a cache folder, and links them in the current project or working directory. This way, rJavaEnv does not contaminate the user’s machine with unnecessary installations and configurations.
When downloading a Java version, it tells you where it’s stored.
Java 21 (amazon-corretto-21-x64-windows-jdk.zip) for windows x64 installed at C:\Users\ercbk\AppData\Local/R/cache/R/rJavaEnv/installed/windows/x64/21 and symlinked to C:/Users/ercbk/Documents/rjavaenv/windows/x64/21Code for the path to the installation is then added to your .Rprofile.
“if you are on a Linux system that did not have any ‘Java’ version previoulsy installed and you are not using pre-build ‘R’ package binaries (for example from ‘Posit Package Manager’) and instead install all ‘R’ packages from source, after this step you may have to quit R, follow these steps: https://solutions.posit.co/envs-pkgs/using-rjava/#reconfigure-r to set configure ‘Java’ for ‘R’, and only then install ‘rJava’, as otherwise ‘rJava’ cannot be built from source.”
- {rJavaEnv} - Aims to assist users of all {rJava}-dependent packages by providing functions to quickly install the required Java version and set environment variables.
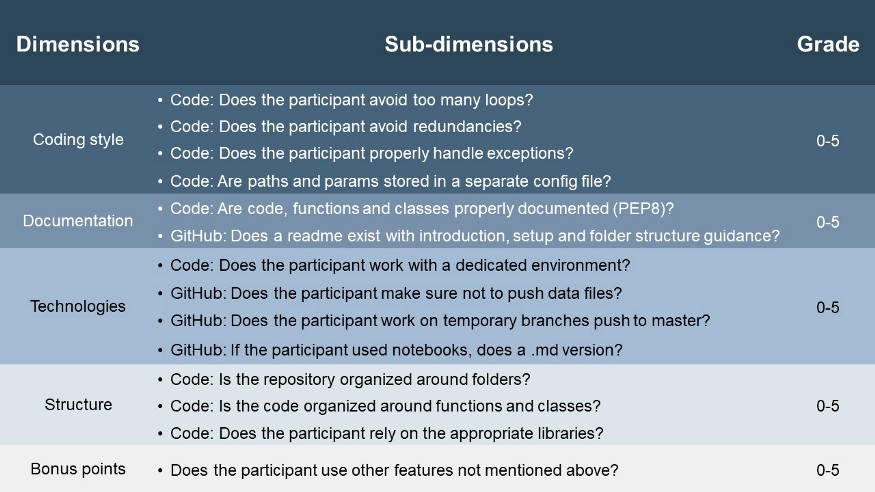
Hackathon Criteria
Update R
- Misc
RStudio NEW.md
{rig} - r version management system
update.packages(checkBuilt = TRUE, ask = FALSE)is supposed to search for packages in other R versions and update them in the new R version, but I haven’t tried it, yet.Install the newest stable version to check it out
rig add next R-nextR-<ver>runs a R version without it being the default
Errors when compiling from source may require installing libraries and they’ll supply code to install via “pacman”
- Open Start >> scroll down to RTools40 >> RTools Bash
- Paste pacman code and hit enter to install
Problem packages in the past
- {brms} dependency, {igraph}, didn’t have a binary on CRAN and wouldn’t compile from source even with correct libraries installed.
- Sol’n:
install.packages("igraph", repos = 'https://igraph.r-universe.dev')- installs dev version from r-universe
- Sol’n:
- Some {easystats} packages had gave {pak} some problems. No difficulties using
install.packageswith default repo or if they had a r-universe repo though.
- {brms} dependency, {igraph}, didn’t have a binary on CRAN and wouldn’t compile from source even with correct libraries installed.
- Steps
Copy user installed packages in current R version
In R:
squirrel <- names(installed.packages(priority = "NA")[, 1]) # user installed packages readr::write_rds(squirrel, "packages.rds")- Then, close RStudio
Check/Update rig version
- In powershell:
rig --version - Check current rig release: link
- Download and install if your version isn’t current
- Windows:
winget install posit.rig- Executable (See Assets section)
- Windows:
- In powershell:
Install new version of R
- Close R if not already closed
rig add releaseinstalls the latest version of R.rig default <new_r_version>sets that version as the default- e.g.
rig default 4.4.2
- e.g.
RTools: Check to see if you have the latest because you’ll need it to compile some of newest versions of packages.
- Your rtools folder has the version in it’s folder name.
- rtools website has the latest version and an .exe to download
rig add rtools43will install the RTools for R 4.3 or you can specify any versionrig add rtoolswill install all RTools versions for all R versions that are installed.
Add R and RTools to path
- Right-click Windows >> System >> (right panel) Advanced System Settings >> Environment Variables >> Under User Variables, highlight Path, click Edit >> Click Add
- R: Add path to directory with all the RScript, R exe, etc. e.g. “C:\Program Files\R\R-4.2.3\bin\x64”
- RTools: e.g. “C:\rtools43\usr\bin”
- Right-click Windows >> System >> (right panel) Advanced System Settings >> Environment Variables >> Under User Variables, highlight Path, click Edit >> Click Add
Open R and confirm new version
- If RStudio
- The setting of the new version to the “default” version of R in rig should result in RStudio loading the new version if you have automatic detection enabled.
- If not, Tools >> Global Options >> General
- Under “R version”, click “change” button; choose new R version
- Quit session and restart RStudio
- If RStudio
Install “high maintenance” packages
I’ve had issues with {pak} installing packages that need to be compiled. Maybe be worth trying {pak} first to see if they’ve fixed it.
{cmdstanr} doesn’t live on CRAN, so you have to use:
install.packages("cmdstanr", repos = c("https://mc-stan.org/r-packages/", getOption("repos")))- Check for latest cmdstan version
- After loading the package,
library(cmdstanr), it should run a check on your cmdstan version and tell you if there’s a newer version. - To update, first check toolchain:
check_cmdstan_toolchain()- Might tell you to update RTools or that you need some C++ library added
- Fix C++ toolchain with
check_cmdstan_toolchain(fix = TRUE) - Update cmdstan:
install_cmdstan() - May need to install {rstudioapi} and run
rstudioapi::restartSession()(programmatically) or justctrl + shift + f10so that this package can be used as a dependency for other packages that need to be installed.
- After loading the package,
- Check for latest cmdstan version
{rstanarm}:
install.packages("rstanarm"){polars}, {tidypolars}
Sys.setenv(NOT_CRAN = "true") install.packages("polars", repos = "https://community.r-multiverse.org") install.packages("tidypolars", repos = c("https://community.r-multiverse.org", 'https://cloud.r-project.org'))
Install other packages
moose <- readRDS("packages.rds") moose <- moose[!moose %in% c("cmdstanr", "rstanarm", "ebtools", "translations", "<RStudio add-ins>", "<other pkgs not on CRAN>")] err_pkgs <- list() for (i in seq_along(moose)) { print(moose[i]) tryCatch( expr = pak::pkg_install(moose[i], ask = FALSE), error = function(e) { err_pkgs[[i]] <<- moose[i] } ) } # remove null (or empty) elements of the list leftover_pkgs <- err_pkgs[!sapply(err_pkgs, \(x) is.null(x) || length(x) == 0)] leftover_pkgs fs::file_delete("packages.rds"){ebtools} is my personal helper package.
{translations} is a system package that shouldn’t have been included when I saved the packages from previous version, but was when I recently updated. Might not be necessary to include it in the excuded packages in the future.
Check for updates of RStudio (link)
- Current version under Help >> About Rstudio
- Possible to check for updates under Help >> Check for Updates, but that’s failed me before.
Update Python
Linux
Misc
- Each Ubuntu (and probably other distros) version has a python version already installed. To install a newer but not-the-latest stable version, you have to use the PPA: deadsnakes.
Don’t set the newer version as default. Just include the version in the command, e.g.
python3.12- The pre-installed version of Python has important modules installed that doesn’t come with the deadsnakes versions.
- Even if you do this at the regular user level and not at root, it can still affect scripts (e.g. on PATH) that expect the system-level python version and its modules.
Or set the new python version as an alias in your bashrc.
# add to ~/.bashrc alias python='python3.12' alias python3='python3.12'
- Always a good idea to hang back from the latest version of Python, because of bugs but also because packages like TensorFlow and PyTorch don’t usually support the latest stable version for awhile.
- Each Ubuntu (and probably other distros) version has a python version already installed. To install a newer but not-the-latest stable version, you have to use the PPA: deadsnakes.
Issues
GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) Key Issue
Code
sudo apt update #> Err:4 https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/deadsnakes/ppa/ubuntu jammy InRelease #> The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY BA6932366A755776 #> Get:5 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease [127 kB] #> Reading package lists... Done #> W: GPG error: https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/deadsnakes/ppa/ubuntu jammy InRelease: The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY BA6932366A755776 #> E: The repository 'https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/deadsnakes/ppa/ubuntu jammy InRelease' is not signed. #> N: Updating from such a repository can't be done securely, and is therefore disabled by default. #> N: See apt-secure(8) manpage for repository creation and user configuration details. ############## old way # Import the missing GPG key sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys BA6932366A755776 # Alternative method if the above doesn't work: wget -qO- https://keyserver.ubuntu.com/pks/lookup?op=get&search=0xBA6932366A755776 | sudo apt-key add - # Now try updating again sudo apt update ############## modern way # Remove the old PPA first sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:deadsnakes/ppa # Add the key to the new keyring location wget -qO- https://keyserver.ubuntu.com/pks/lookup?op=get&search=0xBA6932366A755776 | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/deadsnakes.gpg # Add the repository with the specific keyring echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/deadsnakes.gpg] https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/deadsnakes/ppa/ubuntu jammy main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/deadsnakes.list # Update package list sudo apt update- I added the deadsnakes PPA (Personal Package Archive) repository to apt and during the add, it got the error,
ssl.SSLEOFError: EOF occurred in violation of protocol (_ssl.c:2426) - I thought updating and upgrading might help, but I got this error.
- Claude said the key wasn’t imported correctly. The “old way” worked, but it did give me this warning,
apt-key is deprecated. Manage keyring files in trusted.gpg.d instead (see apt-key(8)).- I think this refers to the “modern way” which I also included.
- I added the deadsnakes PPA (Personal Package Archive) repository to apt and during the add, it got the error,
Updating Python
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade # Install software-properties-common if not already installed sudo apt install software-properties-common sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa # check that the new repository was added ls -l /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ sudo apt update sudo apt install python3.12 -y- software-properties-common is a package that has help functions like
add-apt-repository, ppa stuff, gpa key stuff, etc. (It was already came installed with Ubuntu) - The PPA deadsnakes is a repo that has older-than-the-latest python versions for Ubuntu versions.
- The -y flag just says the answer is “Yes” to any prompts
- software-properties-common is a package that has help functions like
Additional Modules
The PPA deadsnakes’ versions seem to be pretty barebones, but the repo also makes available several modules
Absolutely want venv and Claude suggested a few other system-level packages
# Install additional packages you'll likely need sudo apt install python3.12-venv python3.12-dev python3.12-full- dev - Contains Python header files needed to compile C extension
- full - Seems like stuff related to some IDE. Might be one you can skip