Glossary
200 Status - An API serving an ML model returns a HTTP 200 OK success status response code indicates that the request has succeeded.
AMI - amazon machine image. Thing that has R and the main packages you need to load onto the cloud server
Anti-Patterns - certain patterns in software development that are considered bad programming practices.
- As opposed to design patterns which are common approaches to common problems which have been formalized and are generally considered a good development practice, anti-patterns are the opposite and are undesirable.
Arm - a group of patients receiving a specific treatment (or no treatment). Trials involving several arms, or randomized trials, treat randomly-selected groups of patients with different therapies in order to compare their medical outcomes. Experimental arms, which receive an experimental drug, are compared with control arms. Single-arm or non-randomized trials, in which everyone enrolled in a trial receives the experimental therapy
Artifacts - objects that are created as a result of a process. e.g. model objects, cleaned data sets, visuals, etc.
Asynchronous Programming - code runs (or must run) after something else happens and also not sequentially (e.g. when a function calls a callback function in JS).
Athena - amazon query service that works with S3. Best for analyses using kubernetes. ODBC drivers are best with interactive app
B2C, B2B - business-to-consumer, business-to-business, describes a business that’s end-product is being sold to a consumer or a business.
Balanced Design (aka orthogonal) has an equal number of observations for all possible level combinations. For example in an experiment where gender is an independent variable, an equal number of males receive the treatment as do females receive treatment. If the male/female counts were unequal, then the experiment is unbalanced.
- Stat tests have greater power for balanced designs
- Test stat less susceptible to to small departures from the assumption of equal variances (homoscedasticity).
Batch - collect a large number of data points, process them periodically and store results somewhere (contrasts with real-time in which a data input leads to an immediate prediction)
Bindings - Wrapper code that allows you to use a library written in one programming language from another language.
- The bindings essentially translate function calls between languages. When you call an mlpack function from R, the R binding translates your R function call into the appropriate C++ function call, executes the C++ code, and then translates the results back into R data types.
Bootstrapping (CS) - usually applies to a situation where a system depends on itself to start, sort of a chicken and egg problem. (e.g. How do you start an OS initialization process if you don’t have the OS running yet?) Typically a simple file that starts a large process.
Bounce, Email - When an email cannot be delivered to an email server.
- Hard Bounce - indicates a permanent reason an email cannot be delivered (e.g. Recipient email address doesn’t exist; Recipient email server has completely blocked delivery)
- Soft Bounce - indicates a temporary delivery issue (for details on the reasons, see link)
Bounce Rate - the percentage of visitors to a particular website who navigate away from the site after viewing only one page. Low bounce rate can indicate the landing page needs improvement
BPI - Business process improvement is a management exercise in which enterprise leaders use various methodologies to analyze their procedures to identify areas where they can improve accuracy, effectiveness and/or efficiency and then redesign those processes to realize the improvements.
Burst Reporting - Automated generation of multiple personalized reports from a single template. Instead of creating one giant report, the system produces individual reports tailored to each store, time period, or business unit. This is essential for enterprises that need to distribute customized reports to multiple stakeholders.
C++ Headers - Files containing declarations (function prototypes, class definitions, constants, etc.) without the actual implementation code. They typically have
.hor.hppextensions. Traditional C++ libraries separate declarations (in headers) and implementations (in separate .cpp files that get compiled into binary libraries).- A “header-only library” like mlpack means that all the code — both declarations AND implementations — is contained entirely in header files. These are convenient because you just need to include the headers in your project without linking to separate compiled libraries.
CAC - customer acquisition cost - measures how much an organization spends to acquire new customers. The total cost of sales and marketing efforts, as well as property or equipment, needed to convince a customer to buy a product or service.
CapEx - Capital Expenditure - 1 of 2 main forward budgeting mechanisms for a corporation (also see OpEx). Often used to undertake new projects or investments or large-scale asset acquisitions (buildings and vehicles)
Clinical Trial - research studies (e.g. RCT) performed in people that are aimed at evaluating a medical, surgical, or behavioral intervention
CDI - Customer Data Infrastructure - built to collect behavioral data from primary or first-party data sources, but some solutions also support a handful of secondary data sources (third-party tools)
CDP - Customer Data Platform - add-ons from CDI vendors; a layer on top of CDI that offers a set of capabilities to analyze data using a visual interface.
CDN - content delivery network - a system of distributed servers (network) that deliver pages and other web content to a user, based on the geographic locations of the user, the origin of the webpage and the content delivery server.
CLV/CLTV - Customer Lifetime Value - how much money a customer will bring your brand throughout their entire time as a paying customer.
COGS - Cost of goods sold (aka Cost of Sales) - refers to the direct costs of producing the goods sold by a company. This amount includes the cost of the materials and labor directly used to create the good. It excludes indirect expenses, such as distribution costs and sales force costs.
Complete Factorial Design - a research study involving two or more independent variables in which every possible combination of the levels of each variable is represented. For instance, in a study of two drug treatments, one (A) having two dosages and the other (B) having three dosages, a complete factorial design would pair the dosages administered to different individuals or groups of participants as follows: A1 with B1, A1 with B2, A1 with B3, A2 with B1, A2 with B2, and A2 with B3.
CPD - Continued Professional Development - The time someone spends on structured learning as part of their professional development.
CPG - Consumer packaged goods are items used daily by average consumers that require routine replacement or replenishment, such as food, beverages, clothes, tobacco, makeup, and household products.
CPC - Cost Per Click - refers to the cost an advertiser pays each time an online user clicks on his or her digital ad
CRM - customer relationship management i.e. customer service. Salesforce tracks this data. Example: what features your salesperson promised, and when? How much revenue you have from each customer? Or which salesperson sold the most in the past year?
cron- standard tool used on Unix and Unix-like systems to schedule the periodic execution in the background of a command or script (like a batch script)
Crossed Factors - when every category of one factor co-occurs in the design with every category of the other factor. In other words, there is at least one observation in every combination of categories for the two factors. (in contrast to “nested factors”). As a consequence, interaction terms involving these two factors is allowed.
Crossover Study - A type of clinical trial in which the study participants receive each treatment in a random order. With this type of study, every patient serves as his or her own control. Crossover studies are often used when researchers feel it would be difficult to recruit participants willing to risk going without a promising new treatment.
Cross-Section Data - Randomly sampled data from a population. Like a survey. Aka observational data. See experimental data for comparison.
- Pooled - Differs from panel data in that it is observations of different subjects (instead of the same subjects) in different time periods.
- Rolling - Both the presence of an individual in the sample and the time at which the individual is included in the sample are determined randomly.
- Repeated - Consists of multiple independent cross-sections collected at different points in time. Unlike panel data, where the same individuals are tracked over time, repeated cross-sections draw a fresh sample in each wave.
Cross-Tabs - section of survey analysis where the aggregated results are broken down by demography, party affiliation, etc.
CRUD - Refers to the four basic operations a software application should be able to perform — Create, Read, Update, and Delete.
- In such apps, users must be able to create data, have access to the data in the UI by reading the data, update or edit the data, and delete the data.
- In full-fledged applications, CRUD apps consist of 3 parts: an API (or server), a database, and a user interface (UI).
CTA - marketing term, call-to-action. any device designed to prompt an immediate response or encourage an immediate sale; words or phrases that can be incorporated into sales scripts, advertising messages or web pages that encourage consumers to take prompt action
CTR - click through rate: the ratio of users who click on a specific link to the number of total users who view a page, email, or advertisement. It is commonly used to measure the success of an online advertising campaign for a particular website as well as the effectiveness of email campaigns.
CRM - Customer Relationship Management - acquiring new customers but especially about retaining existing ones
Daypart - The practice of dividing the broadcast day into several parts.
- Example: Restaurants
- Morning (breakfast): This is the first meal of the day, usually from 6 a.m. to 10 a.m. It’s a time when customers are looking for quick, convenient, and often healthier meal options to start their day.
- Midday (lunch): Typically applicable from 11 a.m. to 2 p.m., lunch caters to professionals on work breaks, students, or anyone seeking a midday meal. The focus here is on speed, efficiency, and value for money.
- Afternoon (snack): This period, from 2 p.m. to 5 p.m., often sees a slower pace. Customers might look for a coffee break, a light snack, or a casual meeting spot.
- Happy hour: This typically occurs between 4 p.m. and 7 p.m. and allows customers to enjoy discounts on certain drinks, smaller bites, and other cocktail fare. It also enables the restaurant to highlight items that may move slower during other mealtimes.
- Evening (dinner): From 6 p.m. to 9 p.m., dinner is the primary mealtime. Customers often seek a more relaxed and experiential dining atmosphere.
- Late night: Extending from 9 p.m. onward, this menu caters to night owls, offering anything from full meals to snacks and drinks.
- Example: Restaurants
DAU - daily active users, ex: daily avg # of registered users of the site over past 30 days
DBA - Database Administrator is an admin role that understands the particular database technology and how to get the best out of it. This includes improving performance, backups and recovery.
DDL - Data definition or description language - Subset of SQL. Used to:
- Keep a snapshot of the database structure
- Set up a test system where the database acts like the production system but contains no data
- Produce templates for new objects that you can create based on existing ones. For example, generate the DDL for the Customer table, then edit the DDL to create the table Customer_New with the same schema.
Desparate Impact Analysis - Analysis of the result of the application of a standard, requirement, test or other screening tool used for selection that—though appearing neutral—has an adverse effect on individuals who belong to a legally protected class Differential Dropout**]{style=‘color: #009499’} - Differing dropout rates between treatment arms
DMA - Designated Market Area; a geographic region where Nielsen, the ratings company, analyzes and quantifies how television is viewed. Residents can receive the same local TV and radio stations
DNS - Domain Name System**]{style=‘color: #009499’} - translates domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
DSL - domain-specific language - a computer language specialized to a particular application domain
EMR - Amazon version of a spark cluster used for big data processing and analysis.
Endogenous - A model variable is correlated with other variables excluded from the model (omitted variable bias). Determined by measuring the correlation between the variable and residuals of the model. If a predictor variable hasn’t been randomly assigned, it’s likely to be endogenous.
Equitability - concept that says a dependence measure should give equal importance to linear and nonlinear relationships. Consistent strength measurements across different variable relationships that have similar amounts of noise.
ERP - enterprise resource planning, sort of a catch-all for manufacturing, supply-chain, etc, see the wiki
ETL - extract, transfer, load - usually refers to transferring data from one location to another
Endpoint (biostats) - Outcome variable measured in a medical study. e.g. Death, stroke, or quality of life are good endpoints. Blood tests and images on scans are not good endpoints.
- A composite endpoint is one that consists of two or more events
- Example: death due to cardiovascular causes or hospitalization due to heart failure
- So the binary outcome would be a 1 if either of those events took place or a 0 if they did not. Or in a survival model, time until either of those events.
- Example: death due to cardiovascular causes or hospitalization due to heart failure
- A composite endpoint is one that consists of two or more events
EOF - End of file - Input from a terminal never really “ends” (unless the device is disconnected), but it is useful to enter more than one “file” into a terminal, so a key sequence is reserved to indicate end of input.
ex ante - based on assumption and prediction and being essentially subjective and estimative
ex post - based on knowledge and retrospection and being essentially objective and factual
Experimental Data - data from a RCE/RCT. Compare with observational data
FaaS - Function as a service - type of cloud service for developing, running, and managing apps (e.g. AWS Lambda)
Factorial Design - Experiment where you’re interested in the effect of two or more independent variables.
Fraud Rules - fraud scores are calculated based on rules, which add or subtract points. The user action may be a transaction, signup or login. Rules look at data points such as an email address, IP address, or social media presence.
Fraud Score - assigned values to how risky a user action is. Scoring determined by fraud rules.
Fuzzy Design - See Sharp Design
GHA - Github Actions
GMV - Gross merchandises value - the total value of merchandise sold over a given period of time through a customer-to-customer (C2C) exchange site
GRP - Gross Rating Point. A standard measure in advertising, it measures advertising impact. You calculate it as a percent of the target market reached multiplied by the exposure frequency. Thus, if you get advertise to 30% of the target market and give them 4 exposures, you would have 120 GRP.
HTE - Heterogeneous Treatment Effect - Also called differential treatment effect, includes difference of means, odds ratios, and Hazard ratios for time-to-event outcome vars
- Ascertaining subpopulations for which a treatment is most beneficial (or harmful) is an important goal of many clinical trials.
- Outcome heterogeneity is due to wide distributions of baseline prognostic factors. When strong risk factors exist, there is hetergeneity in the outcome variable.
- Solution: add baseline predictors to your model that account for these strong risk factors.
- Heterogeneity of Treatment Effects - The degree to which different treatments have differential causal effects on each unit.
Hit Ratio - percent of records that were read in order to complete a query in a database. Cloud db providers often charge by the number of records searched
Homogeneity of Treatment Effects - See Heterogeneity of Treatment Effects
HPC - High Performance Computing
Honeypot - data (for example, in a network site) that appears to be a legitimate part of the site, but is actually isolated and monitored, and that seems to contain information or a resource of value to attackers, who are then blocked.
Hypertoroidal Data - Data recorded as angles . Angular observations are often jointly observed with other angular observations, forming what is referred to as hypertoroidal data.
- Examples include wave directions in environmental science, directions of animal movement in biology, dihedral angles in protein backbone structures in bioinformatics, and times of crimes in political science.
IaaS - infrastructure-as-a-service ( Hardware is provided by an external provider and managed for you)
IAM - identity and access management, keys and passwords etc
Interval Data - A data type which is measured along a scale, in which each point is placed at equal distance from one another. Interval data always appears in the form of numbers or numerical values where the distance between the two points is standardized and equal. (source)
- Doesn’t have a defined absolute zero
- Cannot be multiplied or divided, however, it can be added or subtracted.
- Also see Ratio Data
IRB - institutional review board, reviews studies ethical and moral issues
ITT - Intent-to-Treat analysis includes all randomized patients in the groups to which they were randomly assigned, regardless of their adherence with the entry criteria, regardless of the treatment they actually received, and regardless of subsequent withdrawal from treatment or deviation from the protocol. Avoids overoptimistic estimates of the efficacy of an intervention resulting from the removal of non-compliers by accepting that noncompliance and protocol deviations are likely to occur in actual clinical practice. So mimics likely situation in the real world, but not good for estimating the causal effect of a treatment.
Kernels - (article) - system kernels - the interface between the operating system, i.e. the software, and the hardware components in a device. It is used in all devices with an operating system, for example, computers, laptops, smartphones, smartwatches, etc.
- When we use a program on a computer, such as Excel, we handle it on the so-called Graphical User Interface (GUI). The program converts every button click or other action into machine code and sends it to the operating system kernel. If we want to add a new column in an Excel table, this call goes to the system core. This in turn passes the call on to the computer processing unit (CPU), which executes the action.
- Jupyter Kernels - an engine that executes notebook code and is specific to a particular programming language (e.g. python kernel)
- Kaggle Kernels - a free platform from Kaggle to run Jupyter notebooks in the browser. Advantage is that you don’t have to set-up an environment locally.
KPI- key performance indicator
KYC - Know-Your-Customer is info a company collects to verify your identity to combat fraud. Used by telecoms and financial services
Lazy Evaluation - ” never pulls data into R unless you explicitly ask for it. It delays doing any work until the last possible moment. It collects together everything you want to do and then sends it to the database in one step.”
Likelihood - probability of seeing this data given a specific value for a distribution parameter (eg mean, sd). Goal is to search for parameter values until the likelihood is maximized.
LOB - Line of Business is a general term which refers to a product or a set of related products that serve a particular customer transaction or business need. (i.e. product categories)
- Examples
- Consumer Banking: credit cards, line of credit or loan program, mortgages, and corporate, small business and personal bank accounts.
- Financial services and brokerages: mergers and acquisitions or partnerships, real estate investments, and wealth management
- Property and casualty insurance companies: property and casualty insurance (i.e., homeowners, car, boat, renters, etc.), life insurance, health insurance, and commercial business insurance.
- Sub-lines of Business would be sub-categories within each LOB
- Examples
Longitudinal Data - See Panel Data
LTV - see CLV/CLTV
Manual Review - A human is reviews the case to determine whether action is needed. In fraud, an model output may trigger a “manual review” to determine whether an event was indeed fraudulent.
Metric Data - Ratio or Interval Data. Non-Metric would be ordinal data
- Also saw “mspline” (non-negative spline) called Metric Data.
MLlib - Apache Spark machine learning library
MVC - Minimum Viable Corpus - a data size threshold; such that below this threshold, the data simply isn’t useful/valuable. Used in data products business.
MVP - Minimum viable project, agile term. Version of a new product which allows a team to collect the maximum amount of validated learning about customers with the least effort
Namespace - Allows you to use two functions with the same name but from different packages, e.g. dplyr::select or in general, package::function. https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3384204/what-are-namespaces/3384384#3384384
NNH - Numbers Needed to Harm - a derived statistic that tells us how many patients must receive a particular treatment for 1 additional patient to experience a particular adverse outcome. Lower NNT and higher NNH values are associated with a more favorable treatment profile.
NNT - Numbers Needed to Treat - a derived statistic that tells us how many patients must receive a particular treatment for 1 additional patient to experience a favorable outcome such as treatment response. Lower NNT and higher NNH values are associated with a more favorable treatment profile.
Nowcasting - Essentially forecasting uising high-frequency data where the forecast is a short period (minutes, hours, etc.) into the future
NPS - Net Promoter Score - a measure of customer loyalty. Widely used market research metric that typically takes the form of a single survey question asking respondents to rate the likelihood that they would recommend a company, product, or a service to a friend or colleague.
NRT - Near real-time, aka streaming data
Observational Data - See cross sectional data
OEM - Original equipment manufacturer
OKR - Objectives and Key Results is a popular management strategy for goal setting within organizations. A framework for turning strategic intent into measurable outcomes for an organization.
Online Machine Learning - A method of machine learning where the model incrementally learns from a stream of data points in real-time. It’s a dynamic process that adapts its predictive algorithm over time, allowing the model to change as new data arrives.
On-Prem - on-premises — working with servers in the the building and not in the cloud.
OOD - out-of-distribution - data which differ from the training data and on which a model might underperform
Open Cohort - subjects can leave or be added over time.
OpEx - Operational Expenditures - 1 of 2 main forward budgeting mechanisms for a corporation (also see CapEx). Relates to day-to-day expenses (such as payroll and software subscriptions). Smaller payouts over time.
Opportunity Sizing - Quantitative analysis to select a subset of ideas to which to devote resources in product development
Nested Factors - happens when all the levels of one factor only occur in combination with one level of another factor (in contrast to “crossed factors”). As a consequence, your model can’t have an interaction term involving these two variables.
P&L - Profit and Loss Statement
Panel Data - aka Longitudinal Data. Cross section data with a time element. Repeated measures of the same subject over time. It allows researchers to analyze changes within those subjects and compare differences between them over time
Parcel - a land record that defines the boundary of a piece of land. These boundaries are the basic administrative unit of local government in regards to land and property. Managing ownership and tax records are the primary reason local governments generate these files. So these are boundaries differentiating ownership of properties.
PEP8 - style guide for python
PI - principal investigator
Pivot Table - Excel name for a
group_by %\>% summarizecalculation- e.g. from a table of individual fruit sales:
group_by(fruit_type, country) %\>% summarize(total_amt = sum(amount))
- e.g. from a table of individual fruit sales:
PLG - Product-led growth is an end user-focused growth model that relies on the product itself as the primary driver of customer acquisition, conversion, and expansion. e.g. open source a product, let the customer go through the documentation and use and experiment with the product on their own time. In contrast to sales pitching a product to a customer and letting them use it for a trial basis.
PM - product manager
PoC - Proof of Concept
POS - point of sale, The point of sale or point of purchase is the time and place where a retail transaction is completed. It can be in a physical store, where POS terminals and systems are used to process card payments or a virtual sales point such as a computer or mobile electronic device.
Ratio Data - Has a defined zero point. Income, height, weight, annual sales, market share, product defect rates, time to repurchase, unemployment rate, and crime rate are examples of ratio data where “zero” means just that. (source)
- The absolute “zero” is treated as a point of origin. In other words, there can be no negative numerical value in ratio data
- Can be added, subtracted, divided, and multiplied
- Also see Interval Data
RCE - randomized controlled experiment, subjects randomly assigned to two groups, treatment and control. Double blind means the researcher doesn’t know who is in which group.
RCT - randomized clinical trial
RDD - Regression discontinuity design
Redis - REmote DIctionary Server - is an in-memory, key-value database, commonly referred to as a data structure server. Used when volume of read and write operations exceed the capabilities of traditional databases. With Redis’s capability to easily persist the data to disk, it is a superior alternative to the traditional memcached solution for caching.
Refactoring - updating or optimizing code
Regression Testing - checks if changes made to a system negatively impacted or broke any of the existing features. It is often performed right after each update or commit to the code base to identify new bugs and ensure that your system works properly.
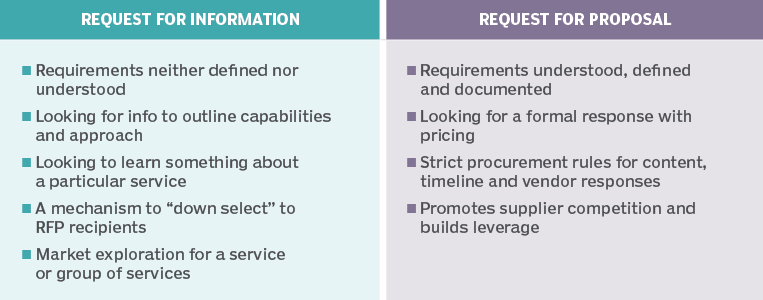
RFI - Request for Information - Used to collect written information about the capabilities of various suppliers. Normally it follows a format that can be used for comparative purposes. An RFI is primarily used to gather information to help make a decision on what steps to take next. RFIs are therefore seldom the final stage and are instead often used in combination with request for proposal (RFP), request for tender (RFT), and request for quotation (RFQ).
RFM - recency, frequency, monetary value - method of estimating customer value; common in retail
RFP - Request for Proposal - A document that an organization, often a government agency or large enterprise, posts to elicit a response – a formal bid – from potential vendors for a desired solution. The RFP specifies what the customer is looking for and describes each evaluation criterion on which a vendor’s proposal will be assessed.
ROAS - return on ad spend
RUG - Regional User Group
S3 - Amazon simple storage service, database
SaaS - Software-as-a-service is a mechanism through which companies offer the functionality of their apps, which remain on their company servers, to other companies or customers.
SCO - sales cycle optimization, active process of providing content on your site (and beyond) that speaks to each of the key phases
SEO - Search engine optimization, generating high page rankings for key search terms
SDK - software development kit
Sharp Design - Each individual or group receives the same “amount” of treatment (e.g. a state law or medication dosage). Opposite being fuzzy design (?)
SKU - Stock Keeping Unit**]{style=‘color: #009499’} - Usually a bar code that has all the information to distinguish it from another product. These attributes can include manufacturer, description, material, size, color, packaging, and warranty terms. When a business takes inventory of its stock, it counts the quantity it has of each SKU.
SLA - service level agreement - a contract between a service provider and its internal or external customers that documents what services the provider will furnish and defines the service standards this provider is obligated to meet. service. Important for holding prediction latency of an app to a certain standard or maintaining data reliability with vendors. (see link for more details on SLA, SLO, and SLI)
SLI - service level indicators - metrics that measure compliance with an SLO (see link for more details on SLA, SLO, and SLI)
SLO - service level objectives - objectives your team must meet in order to meet the conditions of the SLA (see link for more details on SLA, SLO, and SLI)
SMB - (small to medium-sized business) generally defined as companies with fewer than 1000 employees and less than $1 billion in annual revenue.
SME - Subject Matter Experts
SPC - Statistical process control is a method of quality control which employs statistical methods to monitor and control a process
Spill - missed opportunity metric, measures “lost trading days” on which flights or hotels filled too quickly (the result of pricing too low)
Spoil - missed opportunity metric, measures empty seats or rooms (often the result of pricing too high)
SSH - secure shell is a cryptographic Network protocol for operating Network Services securely over an unsecured Network. Typical applications include remote command line login in remote command execution
stdout - standard output, which is the terminal by default
TDD - Test-driven development is a style of programming where coding, testing, and design are tightly interwoven
TF-IDF- stands for term frequency-inverse document frequency, and is often used in information retrieval and text mining.
Throughput - The amount of material or items passing through a system or process, or the number of work items finished per unit of time.
tx - treatment, seen as variable with different treatments as values
URI - Uniform Resource Identifier - a string of characters that unambiguously identifies a particular resource. e.g. s3//bucket/path/to/folder or http://127.0.0.1:5000or c:\Users\me\path\to\folder
UTM - Urchin Traffic Monitor - used to identify marketing channels
- e.g. http://yourwebsite.com/your-post-title/?utm_source=google
- utm code = string after “?”
- This person clicked a google ad to get to your site
- utm code = string after “?”
- Name comes from Urchin Tracker, a web analytics software that served as the base for Google Analytics.
- e.g. http://yourwebsite.com/your-post-title/?utm_source=google
VPS - virtual private server
WIP - Work-in-Progress
Within Person Study - multiple treatments on each person either all in the same period or different treatments in different periods
Year-Over-Year - used to make comparisons between one time period and another that is one year earlier.
- Formula (percentage):
(value_this_year / value_previous_year) - 1 - Example:
(sales_Jul_2023 / sales_Jul_2022) - 1
- Formula (percentage):