Model Context Protocol (MCP)
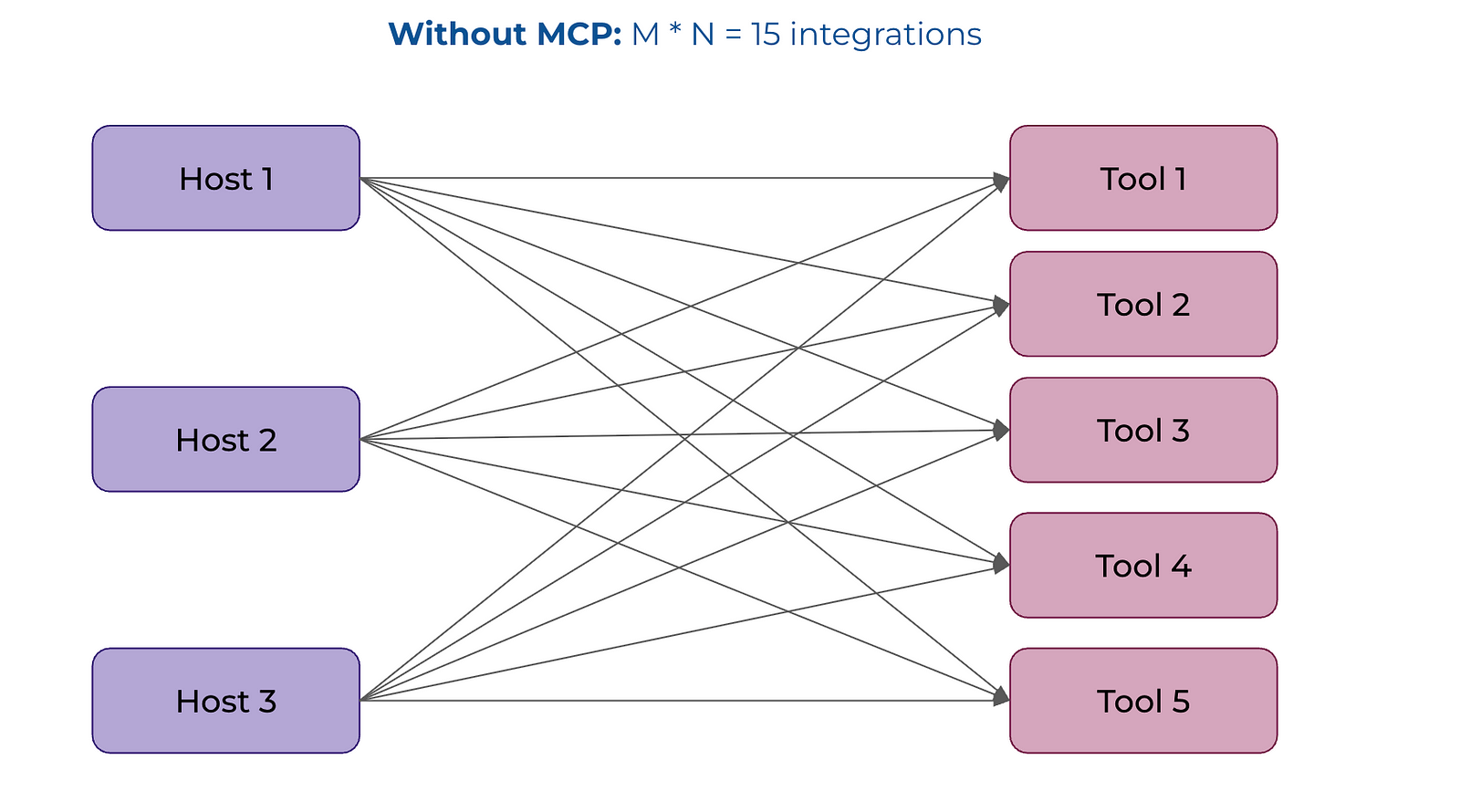
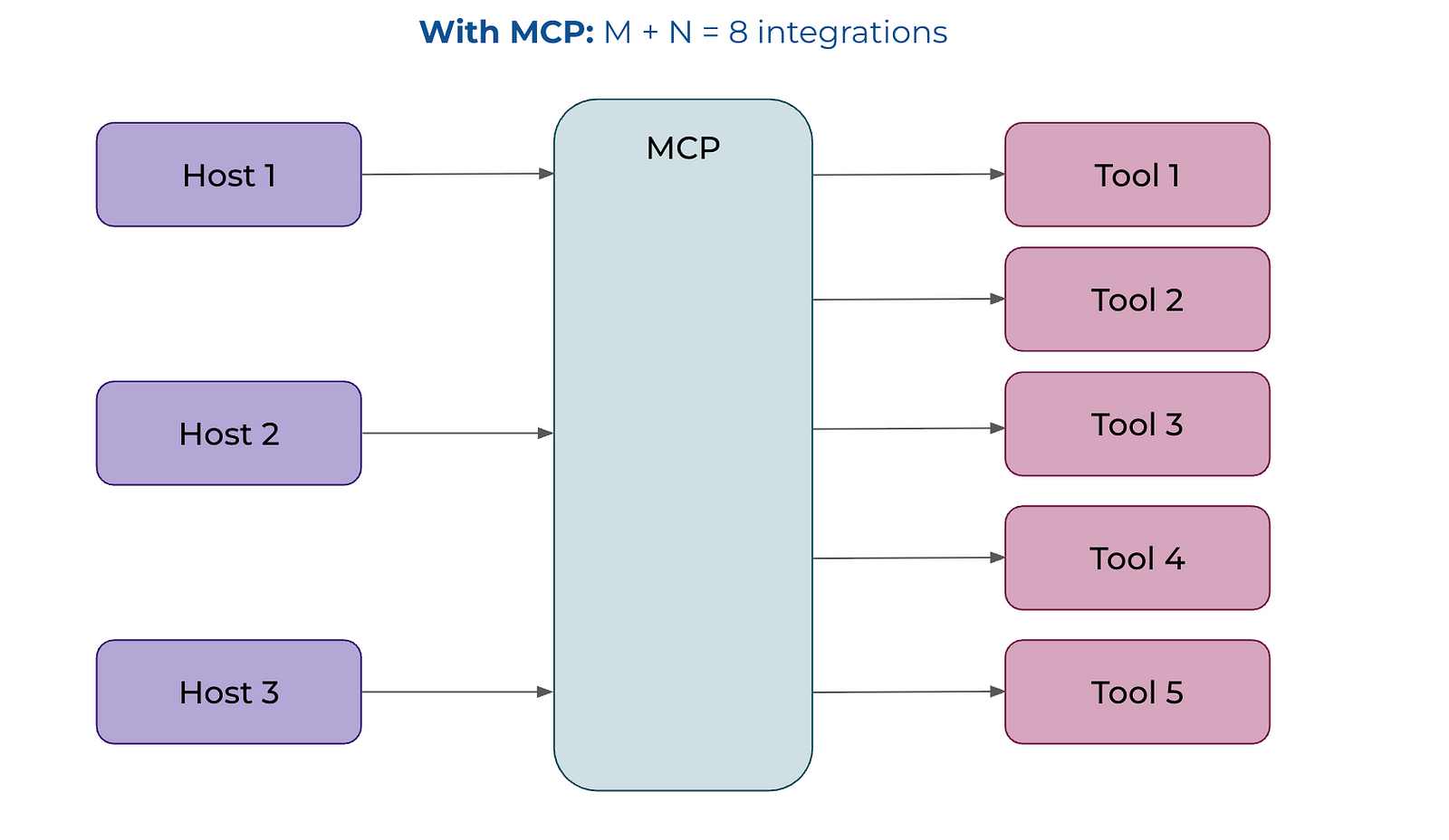
Allows LLMS to more easily integrate with external tools
Notes from MCP (Model Context Protocol): Simply explained in 5 minutes
Packages
- {mcptools} - Allows MCP-enabled tools like Claude Desktop, Claude Code, and VS Code GitHub Copilot can run R code in the sessions you have running to answer your questions
- Works well with {btw}
- {mcpr} - Enables R applications to expose capabilities (tools, resources, and prompts) to AI models through a standard JSON-RPC 2.0 interface. It also provides client functionality to connect to and interact with MCP servers
- {fastapi_mcp} - Exposes FastAPI endpoints as Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools with Auth (i.e. takes an existing FastAPI application and essentially “turning it into” an MCP server)
- {plumber2mcp} - Takes a plumber API and exposes its endpoints as MCP utilities (Same as {fastapi.mcp})
- By adding MCP support to your Plumber API, you make your R functions available as:
Tools: AI assistants can call your API endpoints directly
Resources: AI assistants can read documentation, data, and analysis results
Prompts: AI assistants can use pre-defined templates to guide interactions
- By adding MCP support to your Plumber API, you make your R functions available as:
- {mcptools} - Allows MCP-enabled tools like Claude Desktop, Claude Code, and VS Code GitHub Copilot can run R code in the sessions you have running to answer your questions
Resources
- Docs
- Model Context Protocol servers - Links to official mcp servers and community-based servers
Servers
Claude Skills (not sure what do with these yet)
- Posit Skills for Claude Code (Claude Skills)
- Package development, Testing, Shiny, and Quarto brand_yml, Crafting Release Posts
- Claude Code R Skills: A curated collection of Claude Code configurations for modern R use
- Modular Skills (tidyverse, rlang, performance, OOP, testing)
- Enforcement Rules (security, testing, git workflow)
- Workflow Commands (planning, code review, TDD)
- Context Management Hooks
- Dagster Claude Skills
- Hugging Face Skills - Definitions for AI/ML tasks like dataset creation, model training, and evaluation. They are interoperable with all major coding agent tools like OpenAI Codex, Anthropic’s Claude Code, Google DeepMind’s Gemini CLI, and Cursor.
- Posit Skills for Claude Code (Claude Skills)
Using MCP servers rather than the cloud service CLI tools (e.g. BigQuery CLI) provides better security control over what LLM products (e.g. Claude Code) can access, especially for handling sensitive data that requires logging or has potential privacy concerns.
-
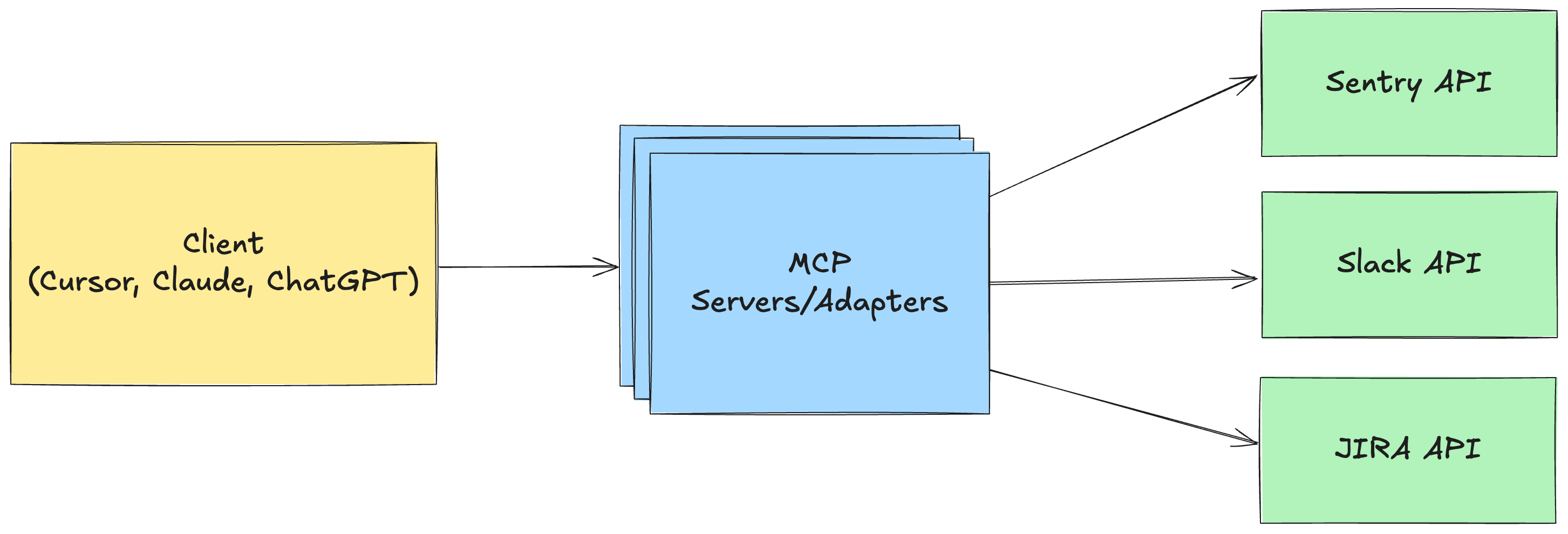
- MCP Client: Various clients and apps you use, like Cursor, know how to talk using the “MCP Protocol.”
- MCP Servers: Providers like Sentry, Slack, JIRA, Gmail, etc. set up adapters around their APIs that follow the MCP Protocol.
- They convert a message like “Get me the recent messages in the #alerts channel” to a request that can be sent to the Slack API
Server File(s) Components
- Defines a set of tools for the MCP Server to implement
- Creates the server to listen for incoming requests
- Defines a `switch` case that receives the tool call and calls the underlying external API, like the Slack API.
- Wire up transport between Client and Server
- Allows the MCP client and server to communicate more simply than standard HTTP requests. Instead, they can read from standard IO when communicating.
Example: Use {btw} to start a local MCP server for your R packages
claude mcp add -s "user" r-btw -- Rscript -e "btw::btw_mcp_server()"- Now Claude Code can answer questions about ANY R package installed on your system.