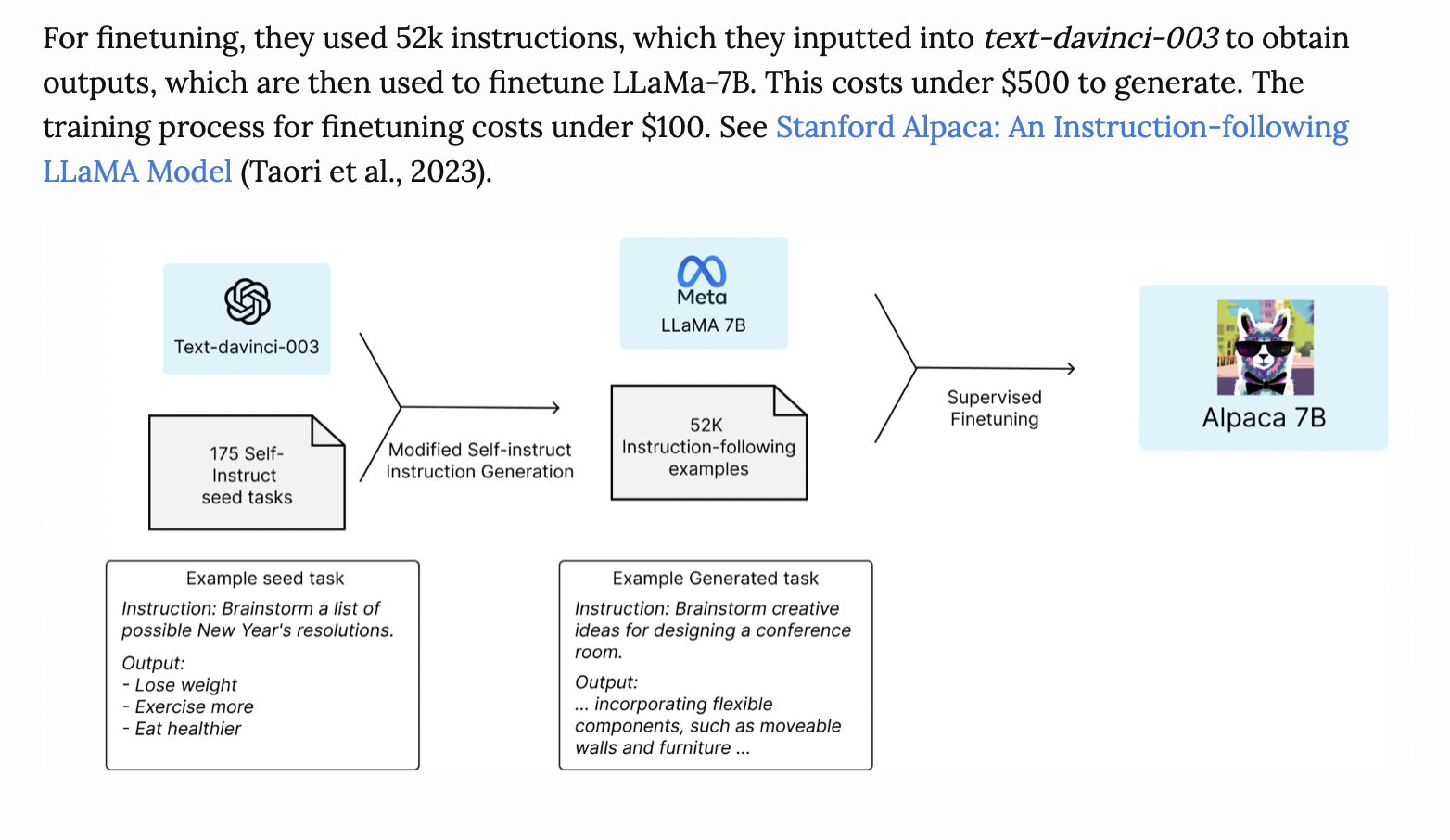
Fine Tuning
Misc
Papers
Resources
minhub - A collection of minimal implementations of deep learning models inspired by minGPT. Each model is designed to be self-contained in a single file with no external dependencies, making them easy to copy and integrate into your own projects.
- These models are particularly suitable for educational purposes, experimentation, and as a starting point for more complex implementations
- Supports loading weights from pre-trained models available in the Hugging Face model hub
- These seem like candidates as base models for fine tuning
Tuning an LLM
- Notes from:
- Hacker’s Guide to Language Models (Howard)
- Stages
- LM Pre-Training - Trained on a large corpus (e.g. much of the internet) to predict the next word in a sentence or to fill in a word in a sentence
- LM Fine-Tuning - Trained on a specific task (e.g. solve problems, answer questions). Instruction Tuning is often used. OpenOrca is an example of a Q&A dataset to train a LM to answer questions. Still predicting the next word, like in Pre-Training, but more target-based on a specific task.
- Classifier Fine-Tuning - Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)is often used. The LLM being trained gives a few answers to a question and then a human or better LLM will pick which one is best.
- Pre-Trained LLMs are ones that are typically the open source ones being released and available for download
- They will need to be Fine-Tuned, but not necessarily Classifier Fine-Tuned. Often times, LM Fine-Tuning is enough.
- Notes from:
Workflow Example (paper)
With ChatGPT, you can have it answer questions from context that contains thousands of documents.
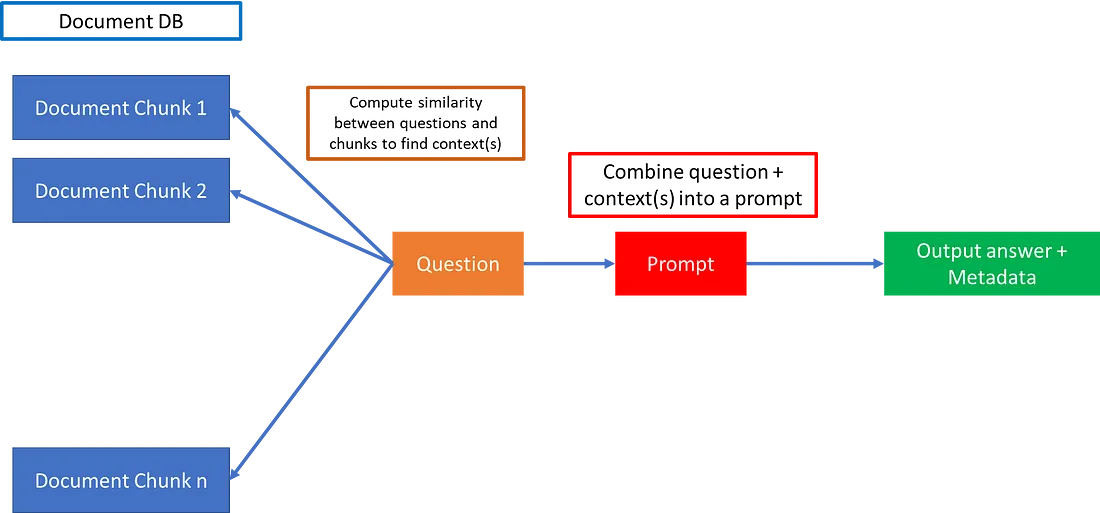
- Store all these documents as small chunks of text (allowable size of the context window) in a database.
- Create embeddings of documents and question
- The documents of relevance can then be found by computing similarities between the question and the document chunks. This is done typically by converting the chunks and question into word embedding vectors, and computing cosine similarities between chunks and question, and finally choosing only those chunks above a certain cosine similarity as relevant context.
- Finally, the question and context can be combined into a prompt as below, and fed into an LLM API like ChatGPT:
prompt=f"Answer the question. Context: {context}\n Question: {question}"